Blog
Top Electronic Cables What You Need to Know
In today’s tech-driven world, electronic cables play a crucial role. These components are essential for connecting devices and ensuring data transfer. A recent industry report indicates that the global electronic cables market is projected to reach $225 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 6.5%. This growth highlights the importance of understanding types like HDMI, USB, and Ethernet cables.
However, not all cables are created equal. The quality can significantly affect performance. Poorly constructed cables can lead to slower data rates and connectivity issues. It’s important to choose the right electronic cables to avoid these pitfalls. Research shows that approximately 30% of consumers experience problems due to improper cable selection.
As technology advances, the demand for high-performance electronic cables increases. Factors such as length, shielding, and connector type are vital. Yet, many users overlook these details. Recognizing what to prioritize can lead to better performance and longer-lasting connections. Taking the time to assess your needs will ensure you select the most suitable electronic cables for your devices.

Top Electronic Cables: An Overview of Types and Uses
When exploring electronic cables, several types stand out. These cables facilitate various devices in both home and professional settings. For instance, HDMI cables are vital for transferring high-definition video and audio. According to industry reports, over 80% of households utilize HDMI cables for their entertainment systems. This dependency highlights their importance in modern electronics.
USB cables are another widespread type, commonly used for data transfer and charging. A recent survey found that nearly 90% of consumers own at least one USB device. Their versatility allows usage across smartphones, tablets, and laptops. However, multiple standards exist, leading to consumer confusion about compatibility. Such issues can lead to frustrations in everyday use.
Analog cables, though less common, still play a role in specific applications. RCA and audio jacks are widely recognized in sound equipment. Experts note a resurgence in analog usage for vintage systems. This trend shows a blend of nostalgia and functionality. Despite their limitations, analog cables provide a unique sound experience that some audiophiles cherish. Balancing old and new technologies can present challenges, yet it enriches the user experience significantly.
Key Specifications and Standards in Electronic Cables
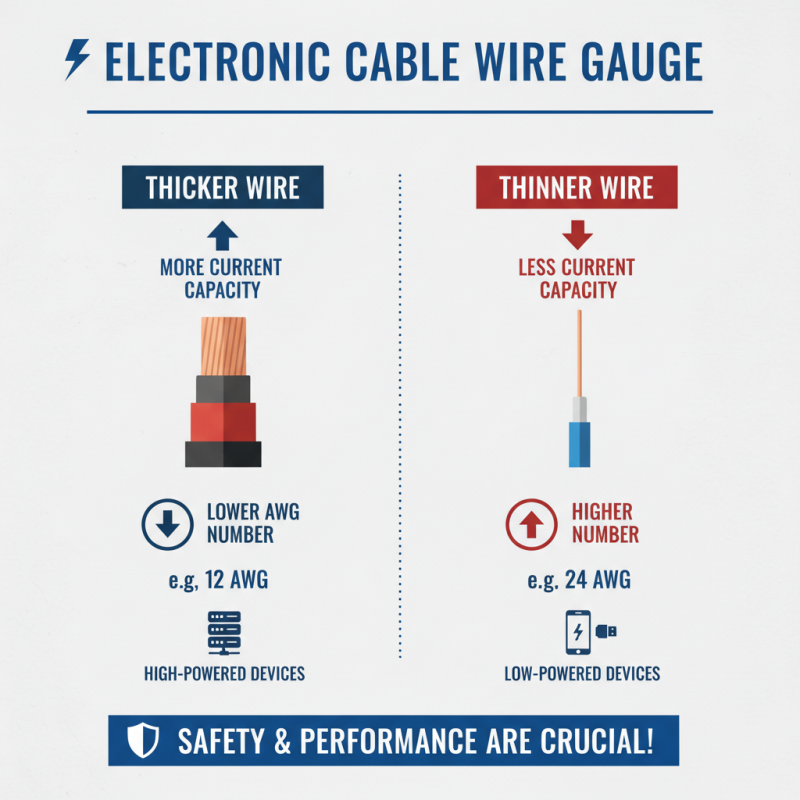
When exploring electronic cables, understanding key specifications and standards is crucial. The wire gauge is fundamental. Thicker wires, often measured in AWG (American Wire Gauge), can carry more current. This can be critical for high-powered devices. A lower AWG number means a thicker wire. For example, a 12 AWG wire can handle more current than a 24 AWG wire. Selecting the right gauge affects performance and safety.
Another important aspect is the cable's insulation rating. Different materials, such as PVC or rubber, determine durability and flexibility. TPR (Thermoplastic Rubber) is often used for outdoor cables due to its weather resistance. It's essential to consider the environment the cable will operate in. Sadly, many overlook this. Using an indoor-rated cable outdoors can lead to failures. Compatibility with standards like UL or IEC ensures safety in various applications.
Twisted pair and coaxial cables serve distinct purposes. Twisted pair is common in data communications. It reduces interference, making transmissions clearer. Coaxial, on the other hand, is ideal for video signals. However, users may sometimes confuse the two and select the wrong type. This leads to connectivity problems that could have been avoided with proper knowledge.
Performance Metrics: Bandwidth, Length, and Signal Quality
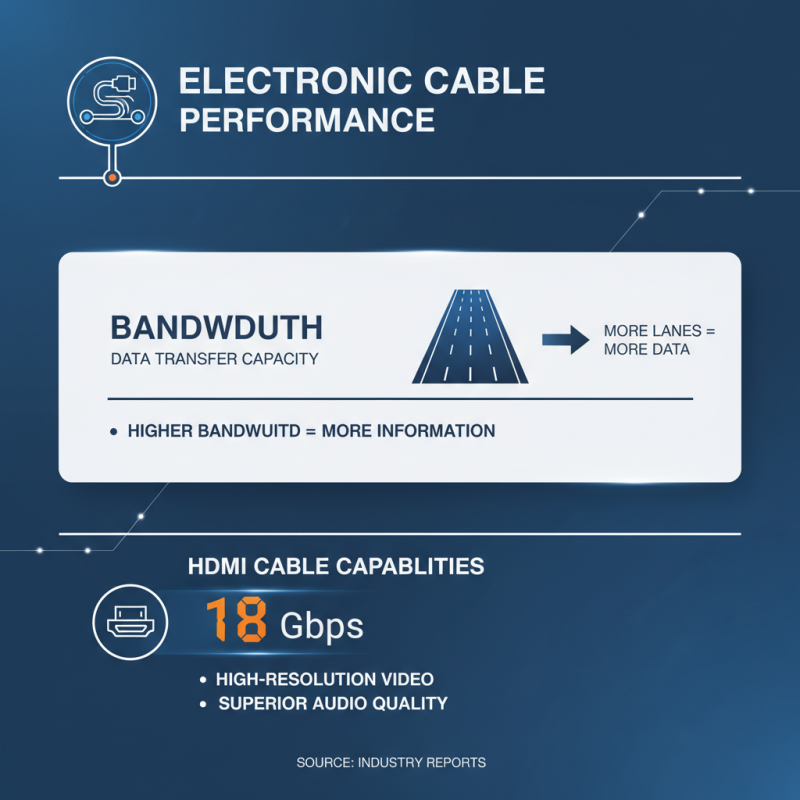
When discussing electronic cables, performance metrics are crucial. Bandwidth defines the data transfer capacity of a cable. Cables with higher bandwidth can handle more information. According to industry reports, a standard HDMI cable can transmit up to 18 Gbps. This allows for high-resolution video and superior audio quality.
Cable length also plays a significant role in performance. Signal degradation occurs with longer cables. A cable exceeding 15 meters may experience diminished signal quality. This can lead to pixelation or audio dropouts in multimedia applications. Data suggests that for optimal performance, keeping cable lengths under 10 meters is ideal.
Signal quality can be influenced by factors beyond just length and bandwidth. Interference from nearby electronic devices can disrupt signals. A study showed that cables with better shielding can significantly reduce interference. For example, cables with triple shielding reported up to 30% less signal loss in noisy environments. Keeping these factors in mind can greatly enhance performance.
Industry Trends: Innovations in Electronic Cable Technology
The electronic cable industry is rapidly evolving. Innovations in technology offer new solutions for connectivity and efficiency. For instance, data from the International Cable and Connectivity Association shows that the market for electronic cables is projected to reach $260 billion by 2026. This growth is driven by increased demand in sectors like telecommunications and renewable energy.
Recently, optical fiber cables have gained attention. They promise higher speeds and better performance compared to traditional copper cables. Reports indicate that optical fiber connections can offer speeds up to 1 Gbps and beyond. However, not all installations are seamless. Many users still face challenges with compatibility and installation processes.
Moreover, eco-friendly materials are emerging. Companies are exploring bioplastics and recyclability in cable production. The environmental impact of cable waste remains a pressing issue. A review by the Global Plastic Alliance notes that about 300 million tons of plastic are produced each year. This raises questions about sustainability in the cable industry and the need for better practices.
Top Electronic Cables - What You Need to Know
| Cable Type | Max Data Rate | Length Range | Key Innovations |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDMI | 48 Gbps | 0.5m - 20m | 8K support, Dynamic HDR |
| USB-C | 10 Gbps | 0.2m - 2m | Power Delivery, Data Transfer |
| Ethernet | 10 Gbps | 1m - 100m | Cat 8 support, Improved shielding |
| DisplayPort | 80 Gbps | 1m - 15m | Multi-Stream Transport, 8K support |
Environmental Considerations: Recycling and Material Sustainability
When we consider electronic cables, the environmental impact cannot be ignored. Research from the International Telecommunication Union shows that e-waste, which includes discarded cables, is expected to reach 74 million metric tons by 2030. This alarming figure highlights the urgency of sustainable practices in cable manufacturing and disposal.
Recycling plays a critical role in reducing the environmental burden. For instance, around 90% of the materials in standard cables can be recovered. Unfortunately, only about 20% of e-waste is currently recycled globally. This gap indicates a significant opportunity for improvement. The materials used in cables often include plastics and metals, which can take hundreds of years to decompose. Failing to recycle contributes to landfills and pollution.
Sustainability in material sourcing is equally essential. Many manufacturers still rely on non-renewable resources. Reports suggest that alternatives like biodegradable materials are on the rise. However, adoption is slow, and some companies prioritize cost over sustainability. As consumers, we should advocate for better practices and support initiatives focused on reducing e-waste.
Top Electronic Cables: Environmental Considerations
This chart illustrates the percentage of different electronic cables that can be recycled and their material sustainability ratings based on common recycling practices.
Related Posts
-

6 Proven Tips for Mastering Wire Assemblies in Your Projects
-

Mastering Wire Puller Techniques: Essential Tips for Efficient Cable Installation and Maintenance
-

Exploring Innovations in Cables and Connectors at China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

Understanding the Importance of Cable Harness Assembly in Modern Technology
-

Ultimate Guide to Cable and Harness Assembly Solutions for Global Procurement Success
-

Essential Checklist for Global Buyers to Navigate the Wire and Cable Industry Trends and Standards
© 2023 JEM Electronics, Inc. – United States Cable Assembly. All rights reserved.

